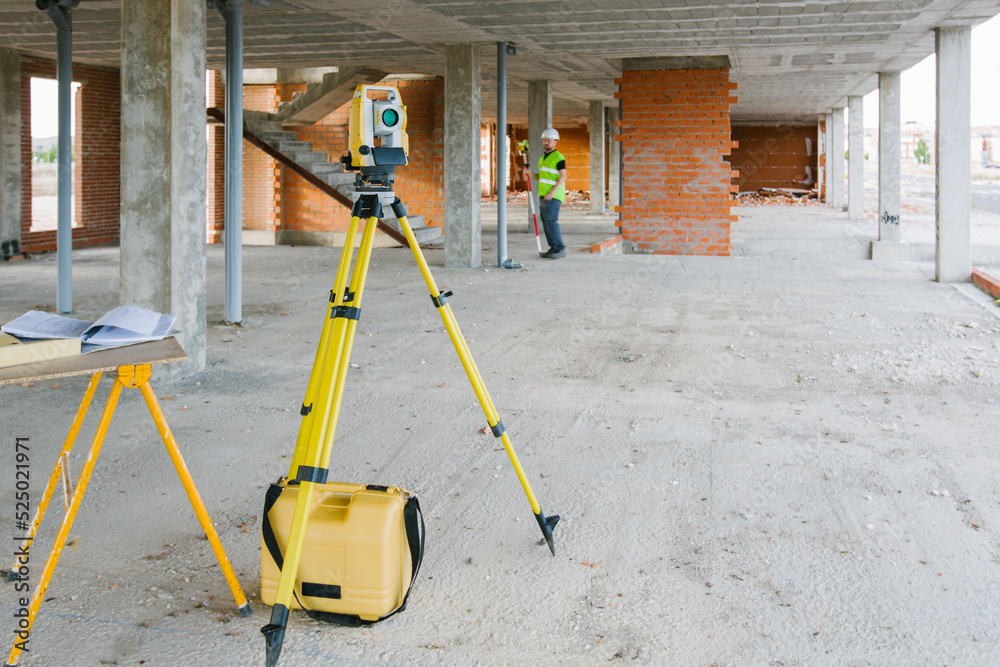
Land surveyors will use different equipment to collect data during a monitoring survey.
Data is collected and analyzed to find out what kind of changes have occurred on the property.
This information can be used by decision-makers who want help protecting their land from problems like erosion or flooding, or making it more useful for farming purposes.
Land surveyors will often use the following equipment during a monitoring survey:
- Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers and antennas
- Inertial measurement unit (IMU) and sensors
- Laser range finders
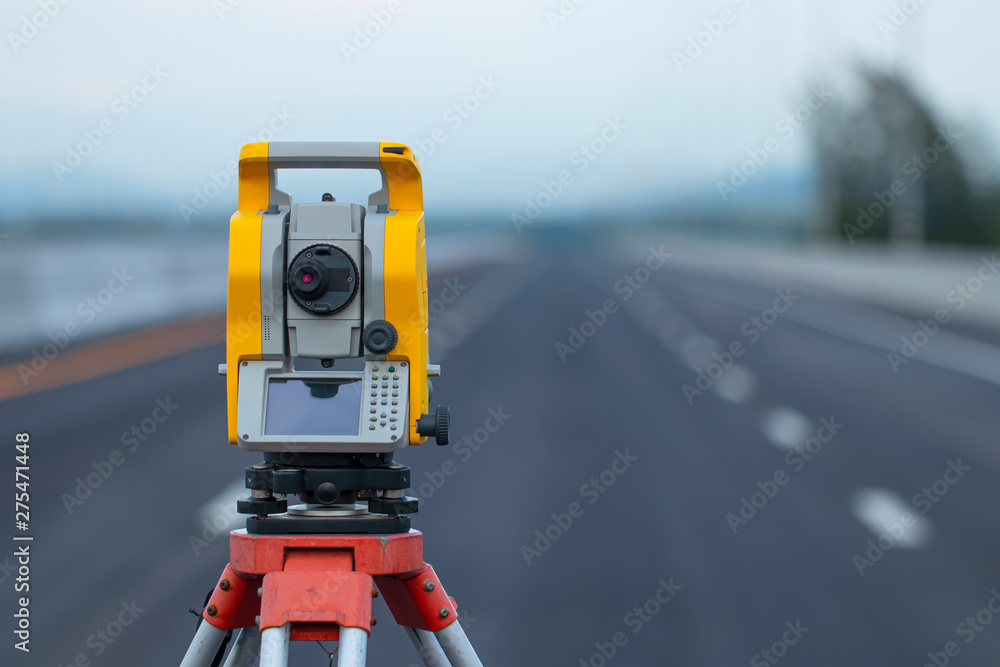
- Total Stations

Why Monitoring Survey Important?
Why Monitoring Survey Important?
Monitoring surveys are important because they help to determine if there are any structural changes in your home, and they can also help you to avoid damages. Monitoring surveys will notify you of any changes on your property or land, so that you can make repairs if necessary. In addition, monitoring surveys can determine whether or not your home is safe and structurally sound throughout the years. The results from a monitoring survey will give peace of mind knowing that all is well with your property.
Why Monitoring Survey Important?
Monitoring surveys are important because they help to determine if there are any structural changes in your home, and they can also help you to avoid damages.
Monitoring surveys will notify you of any changes on your property or land, so that you can make repairs if necessary.
In addition, monitoring surveys can determine whether or not your home is safe and structurally sound throughout the years.
The results from a monitoring survey will give peace of mind knowing that all is well with your property.
History of monitoring deformation survey
Monitoring deformation survey is the process of measuring and recording changes in the shape or size of an object over time.
The purpose of this type of survey is to track movement, usually of man-made structures, in order to assess safety and stability.
Deformation surveys are typically conducted using specialized equipment, such as laser scanners, that can accurately measure small changes in an object’s shape.
Historically, monitoring deformation surveys were first used in the mining industry to track the movement of tunnels and shafts.
This type of surveying was later adopted by the engineering and construction industries to track the settlement of buildings and other structures.
In recent years, monitoring deformation survey has become an important tool for disaster response and risk management.
For example, post-earthquake surveys have been used to assess damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Methodology of Monitoring Survey
A monitoring survey is a way to assess the effectiveness of your project.
It’s not actually a survey; it’s more like an analysis of data over a period of time and from a baseline with the aim to inform decision-making to warn/flag movements.
The results of a monitoring survey help you understand how well your project has been implemented and what might need improvement or change.
A monitoring survey report summarizes the findings and may include recommendations for improvement based on those findings.
The results of a monitoring survey help you understand how well your project has been implemented and what might need improvement or change.
A monitoring survey report summarizes the findings and may include recommendations for improvement based on those findings.
Monitoring surveys are often used as part of a larger evaluation, but they can also stand alone as an independent evaluation tool when conducted by experienced evaluators who have experience working in developing countries, especially those with low levels of data availability and reliable sources for collecting primary data (such as quantitative or qualitative research).
There are many different types of monitoring surveys that all have their own benefits, disadvantages and applications depending on what information you’re trying to collect about your program.
Equipment Used in Monitoring Survey
- GPS (global positioning system)
- Total station
- Geodimeter
- Laser scanner
- Bathymetric survey equipment, such as echo sounder, depth sounder and side scan sonar.
- Surveyor’s chains and levels are used to measure the height of an object.
- Tape measures, protractors and compasses are also used in monitoring surveys.
Monitoring Survey is used to provide information on the deformation of structures and can be used to predict future problems.
Monitoring surveys are used to collect information on the deformation of structures and can be used to predict future problems. The monitoring survey is a technique that uses geodetic instruments and techniques for monitoring ground movements, displacements in buildings, foundation walls or slopes.
What Information to Collect on a Monitoring Survey?
What is deformation monitoring surveys?
Monitoring surveys are used to measure the deformation of structures. A monitoring survey is a non-destructive geotechnical investigation that provides information on the current state of stress in a structure, helping to predict future problems and determine if a structure is safe. Monitoring surveys can also be used to detect changes in the structure over time, such as settlement or movement caused by erosion or earthquakes.
Deformation monitoring surveys are typically used when there is no access to the interior of buildings and structures for other types of investigations or inspections (e.g., boreholes).
How is monitoring the deformation survey done?
There are a few ways to monitor deformation:
1. Ground-based LiDAR (also called terrestrial laser scanning or TLS) can be used to track changes in the shape of objects over time. This method is often used to monitor buildings, bridges, and other structures for any deformations that may occur.

2. GPS can also be used to track ground movement over time. This method is often used in areas where there is a lot of tectonic activity, such as near fault lines or volcanoes.
The Different Types of Monitoring Surveys
3. In some cases, satellites can also be used to monitor deformation from space. This method is useful for large areas or for monitoring remote locations where it would be difficult to set up ground-based equipment.
A static monitoring survey is a type of monitoring survey that measures the effects of construction on existing structures. A static monitoring survey identifies existing building movements and structural changes before, during and after construction.
Deformation surveys utilize specialized instruments to measure changes in the shape of a structure over time.
Geodetic surveys use Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology to record baseline positions before and after construction.
Construction monitoring surveys monitor site activities such as grading, excavation work and material placement during construction projects.
Geotechnical monitoring surveys are used to evaluate subsurface conditions prior to excavation and determine whether additional soil investigation is needed for deeper foundations or walls with increased lateral pressures.
The different types of monitoring surveys include:
- Static Monitoring Survey–Static monitoring surveys identify existing building movements and structural changes before, during and after construction.
- Deformation Monitoring Survey–Deformation surveys utilize specialized instruments to measure changes in the shape of a structure over time.
- Geodetic Monitoring Survey–Geodetic surveying refers to any type of surveying system that uses GNSS signals from satellites or ground antennas (base stations).
- Construction Monitoring Survey–Construction monitors generally focus on measuring time-dependent phenomena like settlement levels at critical points within an excavation site.
Construction Monitoring Survey
Construction monitors generally focus on measuring time-dependent phenomena like settlement levels at critical points within an excavation site.
Geotechnical Monitoring Survey
This type of survey analyzes subsurface conditions prior to excavating into them by measuring undisturbed soil properties such as moisture content or density levels.
How to Conduct a Monitoring Survey?
Monitoring surveys are used by organizations to gather information about their programs and services.
The first step to conducting a monitoring survey is understanding the purpose of monitoring surveys.
A good way for you as an organization leader or staff member to get started with your own monitoring survey is by conducting research about similar programs in other countries, states or provinces.
Who Conducts Monitoring Surveys?
Organizations, such as leadership and staff members, conduct monitoring surveys.
Conducting research on similar programs in other countries, states, or provinces can help you understand successful methods and question types for your own survey toolkit.

Long-term contracts may be necessary for cooperation between parties.
The surveyor’s responsibilities include measuring the site and recording its position. A structural engineer assesses how well the building withstands stress, while geotechnical engineers examine the soil at or near the building’s foundation. Civil engineers handle general matters, such as traffic studies and environmental impact reports.
Alternatives to monitoring surveys include ground penetrating radar (GPR), geophysical surveys, and geo-fencing.
Ground penetrating radar (GPR)
Ground penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses high-frequency radio waves to detect subsurface objects. The signals reflect off these objects and return to the receiving antenna, indicating their depth. However, GPR is less accurate than monitoring surveys as it doesn’t directly measure deformation.
Geophysical surveys
Geophysical surveys are used for detecting buried structures, such as pipes or cables, before construction begins. This helps prevent damage to these structures during excavation activities.
Geo-fencing
Microseismic monitoring uses seismic sensors placed throughout an excavation site which detect any vibrations caused by drilling equipment operating near them; this helps determine how much energy was transferred onto surrounding soil layers during drilling operations so workers know how hard they should hit those sensitive areas (i.e., bedrock vs softer soils).
Laser scanning uses lasers mounted on drones flying overhead which measure contours of a given surface allowing engineers see where they should build structures without having contact with any materials themselves—this allows them save costs from having fewer people doing manual labor jobs during construction processes.
Who needs monitoring Surveys?
- Land surveyors: To survey and measure land for the purpose of acquiring, maintaining and disposing of property.
- Property owners: To ascertain the boundaries of one’s own property.
- Land developers: To determine if an area is suitable for development before purchasing it, or to confirm that the work carried out by a construction company has complied with specifications set down by a client.
- Property managers: To ensure that development companies are complying with their contractual obligations regarding maintenance etc., so as not to adversely affect neighbouring properties’ value or enjoyment of their land respectively.
Architects and engineers:
For similar reasons as above, ensuring compliance with plans. In addition, they may need monitoring surveys to establish whether planning permission has been granted correctly by local authorities.
Monitoring surveys can be used at any time. They are most frequently used before construction starts, but they can also be performed after construction is complete or during the life of a structure.
What type of construction projects needs monitoring surveys?
- Buildings – for example, if you are planning to make changes to the structure of your home or office building, you should get a monitoring survey done.
Airports – airports often fall under this category because they are sometimes built on top of older runways as part of an expansion process; therefore, monitoring surveys will need to occur during these processes as well as at other times when work needs doing on the runway itself (such as resurfacing). This is also true for seaports (ports used by ships) which could potentially require similar types of construction projects within their areas throughout time depending on how much business activity occurs there each year; thus making monitoring surveys necessary again during such projects so people don’t accidentally get hurt due too much traffic congestion around trucks carrying heavy materials such as steel beams that would normally weigh over 100 pounds per square foot!
What is construction asset monitoring survey?
What is construction asset monitoring survey?
Construction asset monitoring survey is a process that is used to evaluate and report on the condition of a construction asset (see the section above covering bridges, etc…). Depending on your needs, this process may be conducted by an engineer or land surveyor.
Construction asset monitoring survey is a process that is used to evaluate and report on the condition of a construction asset (see the section above covering bridges, etc…). Depending on your needs, this process may be conducted by an engineer or land surveyor.
The goal of this process is to assess the current condition of your construction assets and determine what measures should be taken in order to preserve their value for as long as possible.
The goal of this process is to assess the current condition of your construction assets and determine what measures should be taken in order to preserve their value for as long as possible.
Why do you need a monitoring survey?
Why do you need a monitoring survey?
Monitoring surveys are used to detect any changes in the land and can be used to predict future problems, such as landslides, erosion, or sinkholes. They can also help prevent damages from occurring. For example, if you are doing a monitoring survey on your property and see that your neighbors’ trees are falling onto your property due to heavy winds, then you may want to consider taking action before they cause any damage.
Monitoring surveys are used to detect any changes in the land and can be used to predict future problems, such as landslides, erosion, or sinkholes.
Monitoring surveys can help prevent damages from occurring and notify you if there are any changes to the land.
A monitoring survey contains critical information about the structure of your property, including any damage or erosion that has occurred.
Monitoring surveys are different from regular surveys in that they include additional information about the structure of your land and where it might be prone to damage.
This information can be critical for preventing damages from occurring or notifying you if there are any changes to the land.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you understand what a monitoring survey is
and how it can benefit your property